Google Safe Browsing on Squid¶
Google Safe Browsing protects proxy clients by showing warnings to users when they attempt to navigate to dangerous sites or download dangerous files. If enabled, every URL accessed through Web Safety is checked by Safe Browsing Update API v4. See Google documentation https://developers.google.com/safe-browsing/v4/ for possible pitfalls and drawbacks of this feature.
Note
Google Safe Browsing APIs are for non-commercial use only. If you need to use APIs to detect malicious URLs for commercial purposes – meaning for sale or revenue-generating purposes – please refer to the Web Risk API. See https://developers.google.com/safe-browsing/v4/ for more information.
In order to enable this module you need to register at Google Cloud Platform and get the Safe Browsing API key. See https://developers.google.com/safe-browsing/v4/get-started for more information. After obtaining the API key type it into the UI / Anti Virus / Safe Browsing / Settings field as indicated on the following screenshot.
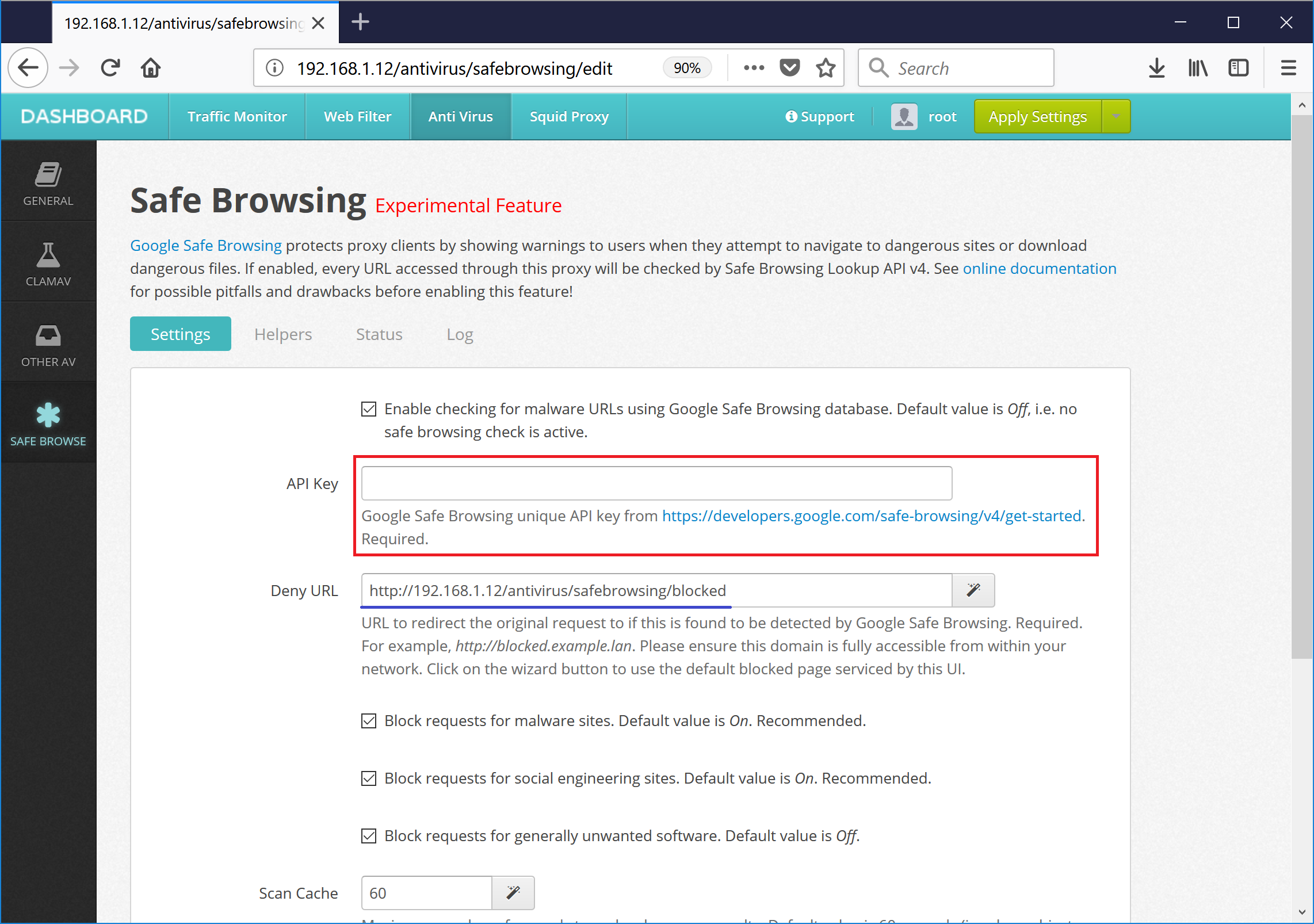
If malicious URL is detected, Web Safety will redirect the proxy user to a new URL. Typically this is some web server deployed in the local LAN that is able to show a page explaining why URL was blocked. This explanation page can also be served by the UI of Web Safety at address http://<ip.of.proxy>/antivirus/safebrowsing/blocked as visible on the above screenshot.
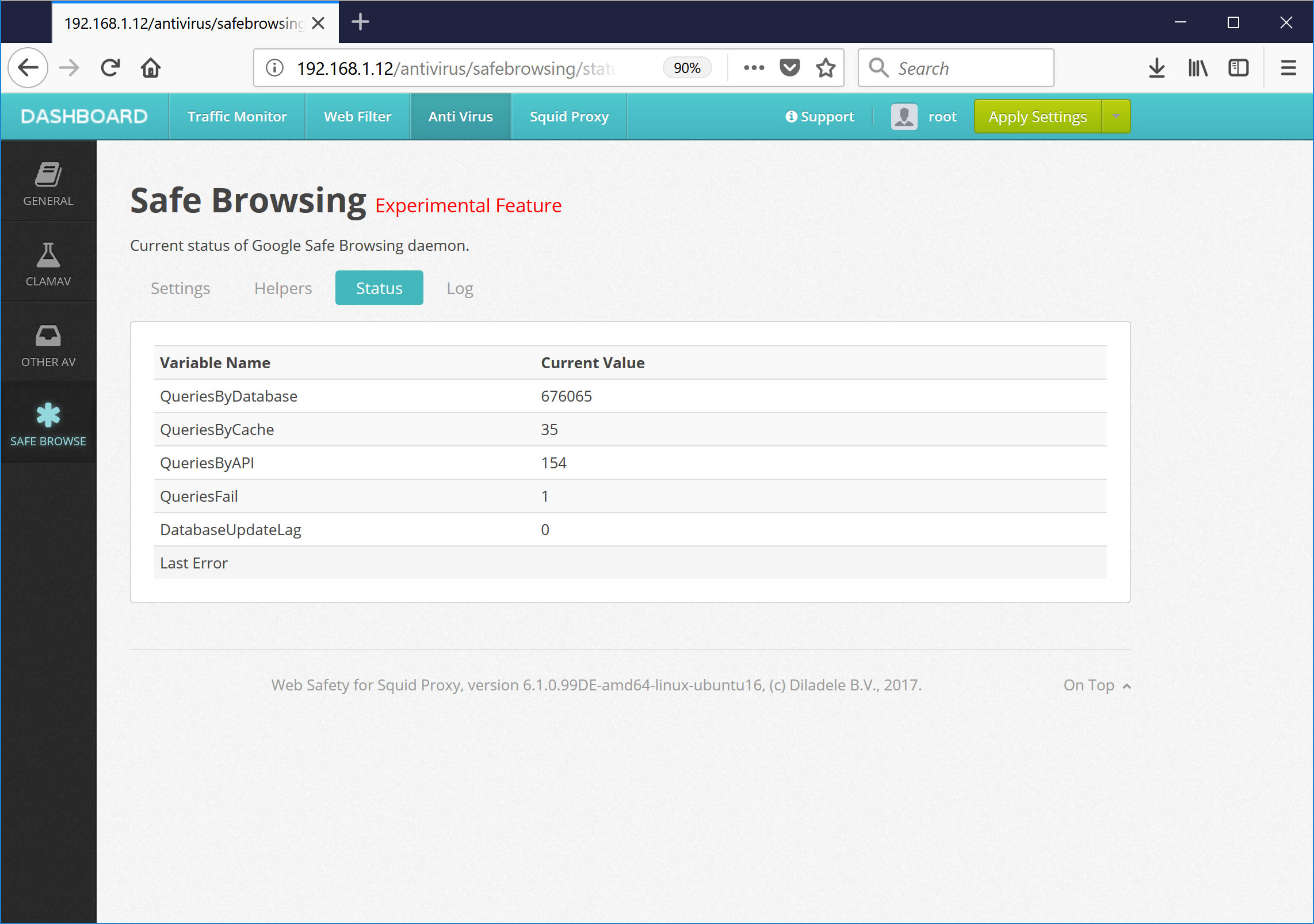
Status and logs of Google Safe Browsing daemon are shown on Status and Log tabs.
Note
In order to test if the Safe Browsing module is indeed activated after configuring it in the UI, try to visit the site used for testing the malware protection called http://www.wicar.org (this is not a real malware site of course). Your browser should show a blue blocked page of Web Safety.